Routine STI testing is recommended for all women having abortions because:
- STIs often have few or no symptoms, so testing might be the only way to find out if you are infected
- Many STIs are easily treated, but if left untreated may become painful or cause long term health problems
- Some STIs increase the risk of suffering post-abortion infection

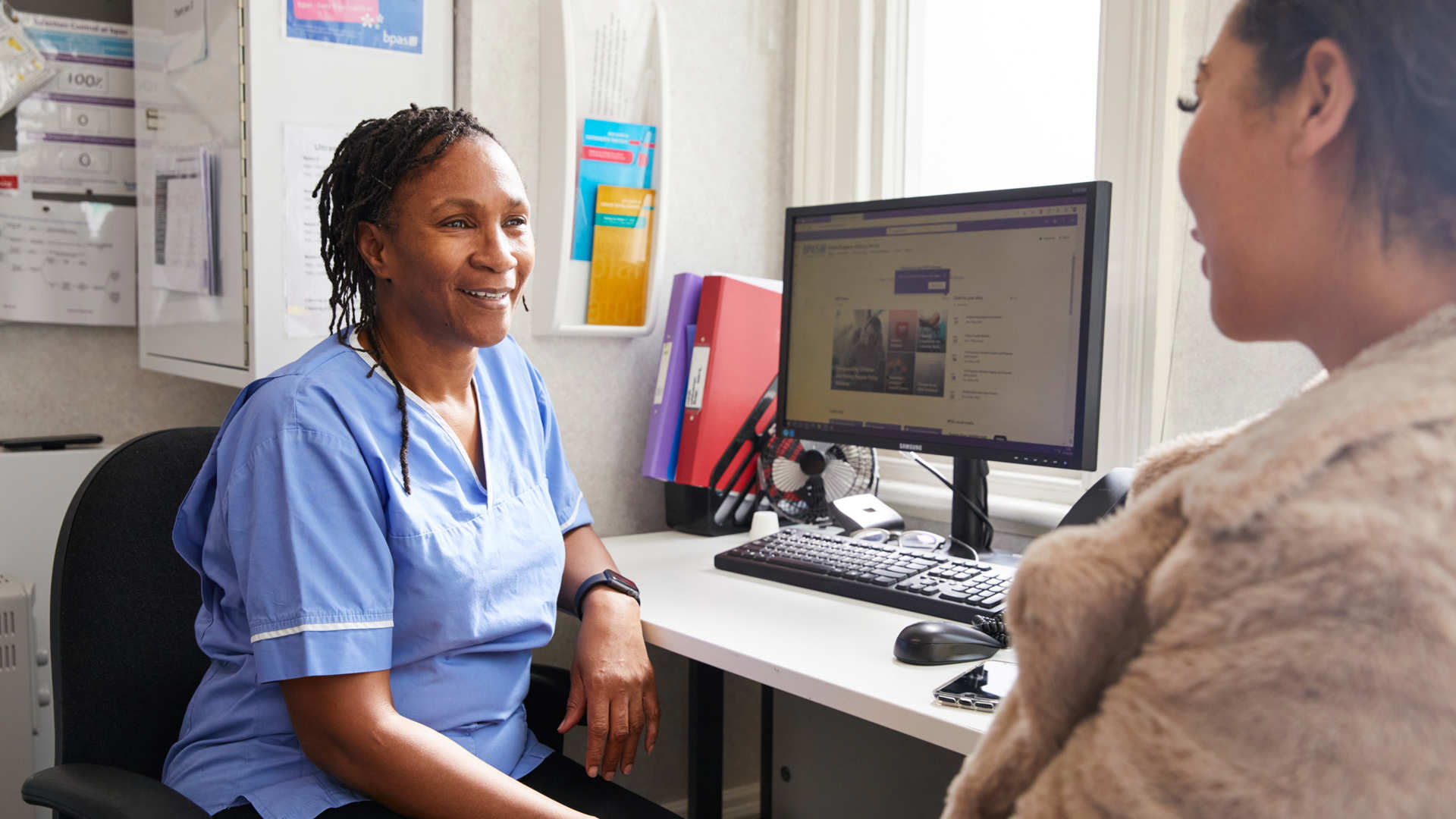
BPAS STI testing in clinic
We will explain which tests we can offer you as part of your NHS funded treatment. The tests are quick and convenient - a swab or urine test and blood sample is all we need. We may offer you a test for:
- Chlamydia
- Gonorrhoea
- HIV
- Syphilis
If you are paying for your own treatment and want to be tested for STIs, ask your nurse or healthcare professional for costs. They can also tell you about local NHS services that provide this service without a fee.
If your are having the abortion pill treatment at home you click here for the details of your postal STI test.
Please don’t take the test if you are bleeding as this will affect the result.
Please read the leaflet carefully and be sure to include the required information clearly on the label provided to ensure that the swab can be processed at the laboratory.

Chlamydia is a common bacterial infection, easily passed on through unprotected sex.
If untreated, it can spread to the womb, fallopian tubes and ovaries, causing pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). PID can lead to lasting pelvic pain, fertility problems and ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy outside the womb). In men, chlamydia can lead to painful infection in the testicles and possible reduced fertility.

Gonorrhoea is a common bacterial infection, easily passed on through unprotected sex.
Untreated gonorrhoea can spread to the womb, fallopian tubes and ovaries causing pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). PID can lead to lasting pelvic pain, fertility problems and ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy outside the womb). In men, gonorrhoea can cause a painful infection in the testicles and prostate gland, and could reduce fertility.

HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a viral infection that weakens the body's ability to fight illness.
Although infection is not common it is still important to be tested because the earlier a diagnosis is made, the better the outcome is for those infected with HIV.

Syphilis is a bacterial infection passed on during sex and by skin contact with someone who has a sores or rash caused by syphilis.
It can also be passed from mother to child during pregnancy. Many years of untreated syphilis may cause serious damage to the heart, brain, bones, eyes and nervous system (and can be life threatening).

Confidentiality
We have strict rules to ensure that the information collected about you is kept safe and secure.
You can choose to get your results ideally by text, or email for convenience, or we can call you. We will ask if it is OK for us:
- To leave a message (when we contact you to give you your results)
- To contact the NHS about your results (if we cannot contact you in person)
A password and unique reference number will be agreed at your consultation. This is to check your identity, and confirm that it is safe to discuss your test results over the phone.
If we cannot confirm your identity over the telephone (for example, if you have forgotten your password/reference number), you will be asked to return to the BPAS unit where your tests were done to discuss your results.
Tell us which personal telephone number and email address is best for you to receive your test results in private.

Results
You will be advised of your test results about a week after the samples reach the laboratory.
We will let you know by text or email if your results are negative (which means you do not have an infection).
You will receive a text or email to call the Results Service or the Results Service will contact you by phone if:
- Your test results are positive (which means you do have an infection), or
- Your tests results are unclear (so the test needs to be repeated)
Clients with a positive result of an infection will receive a follow-up call from a BPAS Sexual Health Nurse two weeks after the results are given to ensure they have no concerns and have been able to access treatment.
If your STI result is positive, your recent partners should be contacted so they can get tested and, if necessary, treated. Your partner(s) can be contacted on your behalf without sharing your identity. This may be done by BPAS or your local GUM (Genito Urinary Medicine) Clinic.
BPAS can give you advice and help if you want to contact them yourself.
Although Chlamydia and Gonorrhoea infections can sometimes affect fertility following Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) it doesn’t mean this will happen to you.
Also, there is no evidence to suggest that becoming infected with HIV or Syphilis makes it more difficult to get pregnant.
It is important that you:
- Don't assume that you will not be able to get pregnant after an infection
- Continue to take contraceptive precautions if you do not want to start a family yet

Where else to get tested
It is not possible to return to BPAS for free re-testing after your abortion treatment - but you can get tested for free on the NHS. Find out about testing services below:
- Local NHS Genito Urinary Medicine (GUM) or Contraception and Sexual Health (CASH) services. See www.nhs.uk or www.sexwise.org.uk to find your closest clinic.
- Alternatively you could call the NHS National Sexual Health Helpline on 0300 123 7123
- Your GP
- Brook provides services for those aged under 25, see www.brook.org.uk for details
Free chlamydia testing is more widely available, especially for those aged under 25. It may also available at some pharmacies, youth services, colleges and www.freetest.me
If you prefer to pay for your STI testing, Doctor4U offer a discrete, cost effective service.